MÓDULO II MATEMÁTICAS
- 1. Competencias y Criterios
- 2. Los límites y derivadas, la elipse hipérbola y la distribución binominal
- 2.1. Límite de una función
- 2.1.1. – Actividad 01
- 2.2. Límites laterales
- 2.2.1. – Actividad 02
- 2.3. Cálculo de límites
- 2.3.1. Propiedades de los límites
- 2.3.2. – Actividad 03
- 2.4. Límites de funciones indeterminadas
- 2.4.1. Límites de funciones racionales
- 2.4.2. Límites de funciones radicales
- 2.4.3. – Actividad 04
- 2.5. Límites infinitos
- 2.5.1. Límites en el infinito
- 2.5.2. Límites en el infinito de una función racional
- 2.5.3. – Actividad 05
- 2.6. Funciones continuas
- 2.6.1. Funciones continuas evaluados en un punto
- 2.6.2. Funciones continuas evaluados en un intervalo
- 2.6.3. – Actividad 06
- 2.7. Derivada de una función
- 2.7.1. Definición de la derivada de una función
- 2.7.2. Reglas básicas
- 2.7.3. – Actividad 07
- 2.7.4. Recta tangente
- 2.7.5. Recta Normal
- 2.7.6. – Actividad 08
- 2.8. Cónicas
- 2.8.1. Elipse
- 2.8.1.1. Elementos de una elipse.
- 2.8.1.2. Ecuaciones canónicas de la elipse con centro C(0,0)
- 2.8.1.3. Lado recto y excentricidad de una elipse
- 2.8.1.4. – Actividad 09
- 2.8.1.5. Ecuaciones canónicas de la elipse con centro 𝑪 (𝒉,𝒌)
- 2.8.1.6. – Actividad 10
- 2.8.2. La hipérbola
- 2.8.2.1. Elementos de la hipérbola
- 2.8.2.2. Ecuación canónica de la hipérbola con centro (0,0)
- 2.8.2.3. – Actividad 11
- 2.8.2.4. Ecuación canónica de la hipérbola con centro (h,k)
- 2.8.2.5. – Actividad 12
- 2.9. Distribución binominal
- 2.9.1. Propiedades de la distribución binominal
- 2.9.2. Función de distribución nominal
- 2.9.3. – Actividad 13
- 2.9.4. Uso de tablas de probabilidad pronominal
- 2.9.5. – Actividad 14
- 2.10. Valor esperado y varianza
- 2.10.1. – Actividad 15
- 3. Bibliografía y webgrafía
2. Los límites y derivadas, la elipse hipérbola y la distribución binominal
2.5. Límites infinitos.
2.5.1. Límites en el infinito
- Si la variable x crece o decrece sin cota, y la función f(x) se aproxima a L o M, respectivamente. Estos límites se llaman límites en el infinito y se expresan como:
![]()
- Cuando se escribe x→∞, no significa que en un lugar muy alejado a la derecha respecto al eje x, exista un número más grande que todos al cual se aproxime x. En lugar de esto, se usa x→∞, para indicar que x se hace cada vez más grande sin cota. Para calcular límites en el infinito se tiene en cuenta los siguientes casos:
- Si
 entonces,
entonces, 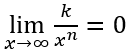 y
y 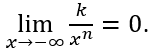 Además, sí
Además, sí 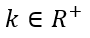 y n es par.
y n es par. 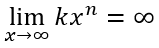 y
y 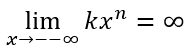 si n es impar,
si n es impar, 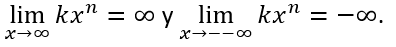
Haga clic en el ejemplo.



